In the field of telecommunications, the use of radio waves is essential for transmitting information wirelessly. Two commonly used bands for radio wave transmission are Ultra High Frequency (UHF) and Very High Frequency (VHF). In this article, we will explore the overview and characteristics of each, highlighting their advantages, disadvantages, and applications.
What is VHF?
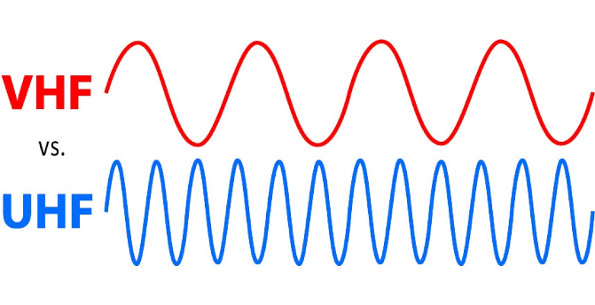
VHF stands for Very High Frequency. It refers to a range of radio frequencies commonly used for various purposes, including communication, broadcasting, and navigation. VHF signals have wavelengths ranging from 1 to 10 meters, corresponding to frequencies between 30 and 300 megahertz (MHz). VHF waves can travel longer distances than UHF (Ultra High Frequency) waves, making them suitable for applications where wider coverage is desired, such as marine communication, air traffic control, and television broadcasting.
VHF waves are widely used in different sectors and industries. Some common applications of VHF include:
- Two-way Radio Communication: VHF frequencies are commonly used for two-way radio communication, such as that used by emergency services, police, and fire departments. VHF radios are also used in maritime communication for ship-to-ship and ship-to-shore communication.
- Television Broadcasting: VHF frequency bands were historically used for analog television broadcasts before the transition to digital broadcasting. VHF channels 2 to 13 (54 to 216 MHz) were widely allocated for TV broadcasting worldwide.
- Air Traffic Control: VHF radio communication is crucial for air traffic control, enabling communication between air traffic controllers, pilots, and ground personnel. VHF frequencies provide reliable communication over long distances, facilitating safe and efficient air travel.
- Amateur Radio: VHF bands are quite popular among amateur radio operators who use them for communication, experimentation, and emergency communication networks.
- FM Radio Broadcasting: FM (Frequency Modulation) radio stations often use VHF band frequencies for high-quality audio transmission. FM radio receivers typically tune into VHF frequencies between 88 MHz and 108 MHz.
What are the advantages of using VHF frequencies over UHF frequencies?
There are several advantages to using VHF frequencies over UHF frequencies in certain applications:
- Longer Range: VHF waves have longer wavelengths compared to UHF waves, which allows them to travel longer distances with less attenuation. This makes VHF suitable for applications that require wider coverage, such as marine communication and air traffic control.
- Better Penetration: VHF waves have better penetration capabilities through obstacles like buildings and foliage compared to UHF waves. This characteristic makes VHF frequencies more suitable for communication in urban or densely forested areas.
- Less Susceptible to Interference: VHF frequencies are generally less congested than UHF frequencies, meaning there is less competition for signal bandwidth. This can result in reduced interference and clearer communication, especially in densely populated areas or areas with high radio frequency activity.
- Efficient Antenna Design: VHF antennas tend to be shorter and more compact compared to UHF antennas, making them easier to install and less susceptible to wind loading. This advantage is particularly significant in applications where antenna size and weight are key considerations, such as handheld radios and portable devices.
- Cost-Efficiency: VHF equipment and infrastructure are often more cost-effective compared to UHF counterparts due to longer wavelength characteristics. VHF-based systems typically require fewer base stations or repeaters to achieve similar coverage, resulting in reduced infrastructure and operational costs.
What about UHF?
Ultra-high frequency (UHF) refers to a range of electromagnetic waves with frequencies between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz). UHF is commonly used for communication purposes; It offers advantages such as shorter wavelength, which allows for smaller antennas and better signal penetration through obstacles like buildings and foliage. UHF radios are widely used in various applications, including broadcasting, two-way communication systems, wireless data transmission, and more.
Common applications where UHF frequencies are preferred over VHF frequencies?
UHF frequencies are preferred over VHF frequencies in various applications due to their unique characteristics. Some common examples of where UHF frequencies are preferred include:
- Two-Way Radio: UHF frequencies are commonly used for two-way radio communication, especially in settings where communication needs to occur within shorter distances, such as warehouse operations, construction sites, and security teams working in buildings or complexes.
- Wireless Microphones and Audio Systems: UHF frequencies are popular for wireless microphone systems due to their ability to transmit audio signals with high fidelity and low interference. UHF frequencies allow for more channels to be available for simultaneous use, minimizing the chance of interference from other devices.
- RFID Technology: UHF frequencies are widely used in Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) systems. UHF RFID tags and readers allow for faster data transfer rates and increased read range, making them suitable for applications like inventory management, supply chain tracking, and access control.
- Satellite Communication: UHF frequencies are utilized for satellite communication, particularly for low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites. UHF signals can be efficiently transmitted and received by relatively small, low-power antennas, making them well-suited for satellite communication systems.
- Remote Control Systems: UHF frequencies are commonly employed in remote control systems, such as for drones, model aircraft, and remote-operated vehicles. UHF signals provide longer transmission range, enabling better control and navigation of these devices.
How do UHF frequencies compare to VHF frequencies in terms of signal quality and interference resistance?
UHF and VHF frequencies have different characteristics when it comes to signal quality and interference resistance.
Signal Quality:
UHF frequencies tend to have more challenges in terms of signal quality compared to VHF frequencies. This is due to a higher susceptibility to signal attenuation, especially in urban areas with obstacles like buildings and other structures. UHF signals have shorter wavelengths, and these shorter wavelengths are more prone to absorption and reflection by buildings, resulting in reduced signal strength and potential signal degradation.
On the other hand, VHF frequencies offer better signal quality in terms of coverage range and penetration through obstacles. Their longer wavelengths enable them to better propagate through buildings, foliage, and other barriers, leading to more reliable signal reception. VHF signals are generally more resilient to signal loss caused by environmental factors.
Interference Resistance:
In terms of interference resistance, UHF frequencies have an advantage over VHF frequencies. The UHF spectrum is typically less congested, providing more available channels with less spectrum interference. This can lead to clearer, more reliable communication with minimal interference and a lower chance of overlapping signals.
VHF frequencies, being lower in frequency, are more prone to interference from other radio sources. The VHF spectrum is often more crowded, especially in densely populated areas where various devices and systems utilize VHF frequencies. This can result in increased signal interference, potential signal collisions, and reduced overall system performance.
It’s important to consider these factors when selecting between UHF and VHF frequencies for a specific application. The choice depends on the specific environment, range requirements, and the prevalence of potential sources of interference.
In summary, VHF refers to a specific range of radio frequencies, typically ranging from 30 to 300 MHz, commonly used for communication, broadcasting, and navigation purposes; whereas UHF refers to range of frequencies between 300 MHz to 3 GHz.
Both UHF and VHF frequency bands have their own characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. UHF is ideal for short-range communication, with better obstacle penetration and reduced interference, whereas VHF is suitable for long-range communication, offering better groundwave propagation.
It’s important to note that the selection of UHF frequencies over VHF frequencies depends on specific requirements, such as range, signal penetration, available spectrum, and interference conditions. Each frequency range has its advantages and suitability for particular applications, and the choice should be made based on careful consideration of these factors.
Having the right choice of communication infrastructure provides clear and smooth connection to your team; it facilitates information circulation and allows for better performance. With UHF and VHF two-way radio products from Al-Shareef Group, your business will achieve greater productivity and ensure worker and customer safety. Reach for Al-Shareef Group for consultancy or any inquires; our team is always ready for help and support.