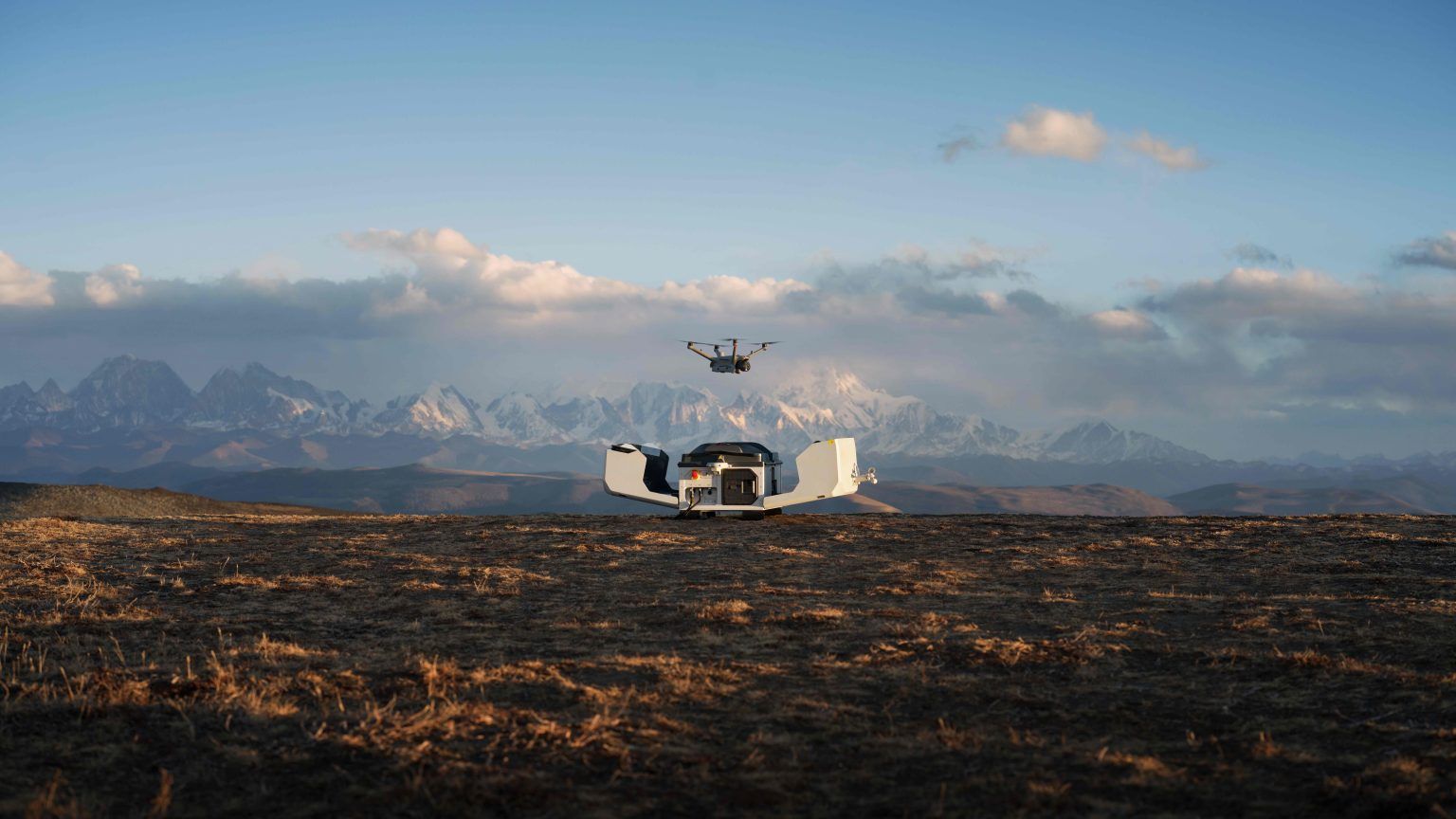
Geo system has revolutionized drone safety at the time it first appeared in 2013. The system progressed from simple flight restrictions to today’s sophisticated 3D no-go zones around runway flight paths and sensitive facilities. This advanced approach has replaced the previous circular structures that blocked restricted areas and now provides more precise protection for critical infrastructure.
The improved geofencing technology now reaches beyond its original boundaries to cover 13 European countries and 19 more nations that didn’t have these safeguards before. The technology will affect drone operations in Saudi Arabia by a lot, especially in urban centers like Dammam, Riyadh, and Jeddah. The system works as an educational tool rather than just an enforcement mechanism. It provides up-to-the-minute information on restricted flight zones and lets operators request unlocks for authorized operations when needed.
This piece explores how the Geo system showcases just one aspect of the fast-changing drone world. We’ll look at new technologies, industry changes, and the challenges that global drone adoption faces in the coming years.
Emerging technologies transforming drones
Advanced technologies are changing how modern drones work, going well beyond basic geofencing systems. AI has become the life-blood of autonomous drone development. These aircraft can now guide themselves without human pilots by using visual sensors and advanced algorithms. Research shows drones notice and interact with their surroundings on their own. They make critical decisions even without GPS signals.
Battery technology has made incredible strides. New state-of-the-art batteries reach an energy density of 410 Wh/kg. This lets drones fly twice as long and cover 70% more distance than regular lithium-ion batteries. These advanced batteries showed amazing results in cold weather. A drone flew for 40 minutes at -20°C, while standard batteries only lasted 10 seconds in similar conditions.
5G connectivity has transformed how drones communicate. It provides reliable, quick connections that drones need to fly beyond what operators can see. Drones now receive and execute commands almost instantly, which means fewer errors during flight. 5G also helps create systems for drones to safely share airspace with regular aircraft.
Scientists have found better ways to make drones more energy-efficient. Their solutions include smarter flight paths, better resource use, and wireless charging with radio frequency or laser beams. A study showed that using genetic algorithms for path planning used 2-5 times less energy than old methods by cutting down unnecessary turns.
Drones share data faster now. The “Dataspace in the Sky” framework lets drones share data securely on 6G networks. It uses federated learning to boost security by sharing models instead of raw data. Up-to-the-minute airspace data creates better awareness and makes it easier for operators to get regulatory approvals through unified platforms.
These advances show a future where drones will work more independently, efficiently, and fit better into both airspace and data systems.
How drones are changing industries
Drones have evolved from experimental tools into valuable business assets that deliver measurable results. These aerial platforms now revolutionize operations in many industries.
Delivery services showcase the impressive capabilities of drones. Companies have achieved one million deliveries in just one year. Modern delivery drones carry up to 10 kg per trip and fly at 120 meters above ground level in designated air corridors. Each delivery reduces carbon emissions by 520 grams compared to traditional road-based methods.
Scientists and researchers make great use of drones for environmental monitoring. The platforms provide more precise geological and topographical information than traditional methods. Drone imagery helps assess riverbank vegetation changes, map river heights, and track erosion with remarkable accuracy. Researchers use thermal cameras on drones to find and count wildlife populations, including vulnerable species like koalas.
Drones are a great way to get compelling advantages for infrastructure inspection. They access hard-to-reach areas of bridges, buildings, and power lines to collect high-resolution visual data and create detailed 3D models. This cuts down inspection time by weeks and reduces or eliminates facility downtime.
Public safety agencies rely more on drone capabilities. These aircraft give vital aerial intelligence during emergencies, boost situational awareness, and improve response times through Drone as First Responder (DFR) operations. Drones have saved 65 people in 27 separate incidents according to one manufacturer’s report.
Agricultural drones with multispectral cameras detect crop stress, diseases, and nutrient deficiencies before human eyes can spot them. They can spray up to 21 hectares per hour in field operations, which makes them much more efficient than traditional methods.
The future looks bright as drone regulations mature and technology advances. These versatile platforms will change many more industries in Saudi Arabia and beyond.
Conclusion
The rise of drone technology marks one of the most important technological changes of our time. Geo and similar geofencing systems have grown from basic flight restrictions into sophisticated 3D navigation tools. Without doubt, this progress shows just the beginning of a broader technological revolution in the drone industry.
Drones now fly longer, make smarter autonomous decisions, and integrate smoothly with existing airspace thanks to AI-powered navigation, next-generation batteries, and 5G connectivity. These capabilities, which seemed impossible just years ago, now benefit delivery services and environmental monitoring.
Drone technology will definitely keep changing faster in coming years. Saudi Arabia is ready to benefit from these breakthroughs, especially when you have cities like Dammam, Riyadh, and Jeddah that could become hubs for drone innovation. Anyone interested in innovative technology can check DJI drones’ latest advances at Alshareef Group, DJI’s partner in Saudi Arabia.
Drones have evolved from simple gadgets to vital tools that change how we work, monitor our environment, and handle emergencies. Their ongoing development promises even greater capabilities if we carefully address the challenges while adopting the opportunities. Drones’ future looks not just promising but truly transformative for businesses, governments, and individuals alike.