The Evolution of Maritime Communication: From Morse Code to LTE
The history of maritime communication is a testament to human ingenuity and technological progress. From the early days of flag signals and Morse code to today’s advanced LTE broadband systems, the methods by which ships communicate with the shore and each other have undergone a remarkable transformation.
In the 19th century, Morse code revolutionized long-distance communication at sea. Ships equipped with telegraph systems could transmit messages over vast distances, albeit at a slow pace. This technology remained the backbone of maritime communication for decades, gradually being supplemented by radio telephony in the early 20th century.
The advent of satellite communication in the 1960s marked another significant leap forward. Suddenly, ships could maintain voice and data connections from virtually anywhere on the globe. However, these systems were often expensive and had limited bandwidth, restricting their use primarily to essential communications.
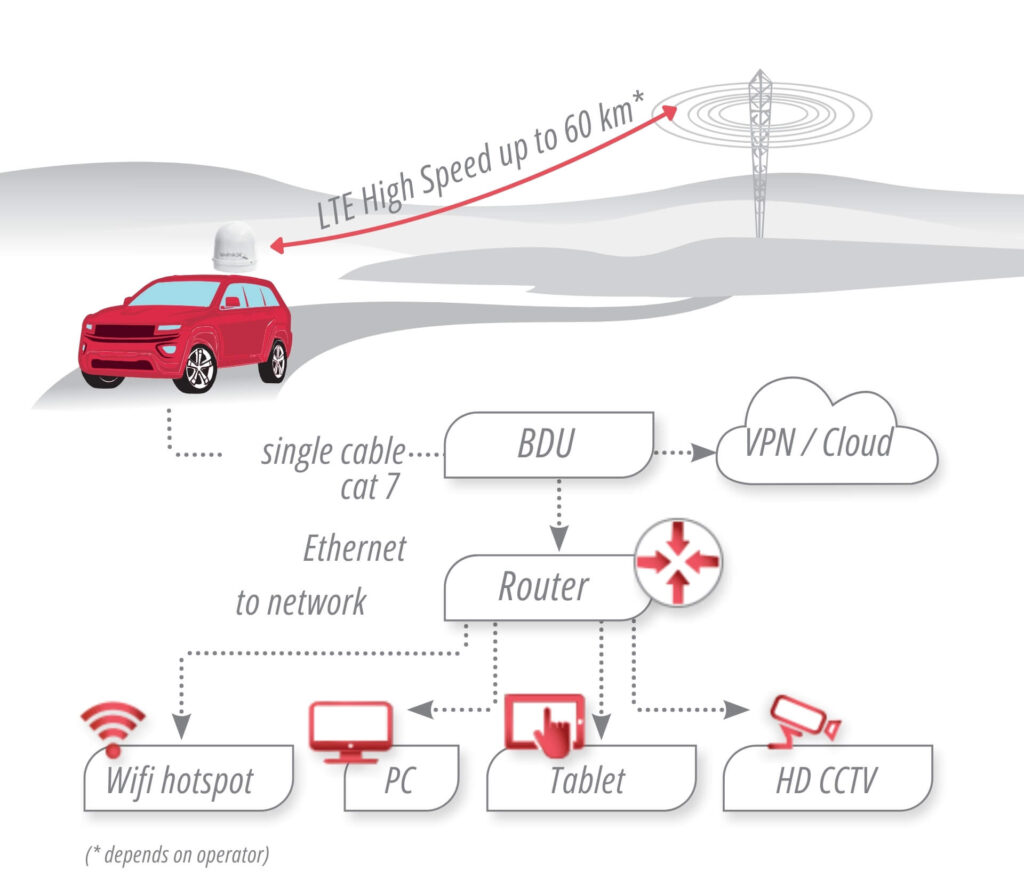
As we entered the 21st century, the demand for more robust and efficient communication systems grew exponentially. The maritime industry, like many others, sought ways to leverage the power of the internet and mobile technologies. This quest for improved connectivity led to the adoption of LTE (Long-Term Evolution) technology at sea, ushering in a new era of high-speed, reliable communication for vessels of all sizes.
Understanding LTE Broadband Antennas: A Game-Changer for Sea Connectivity
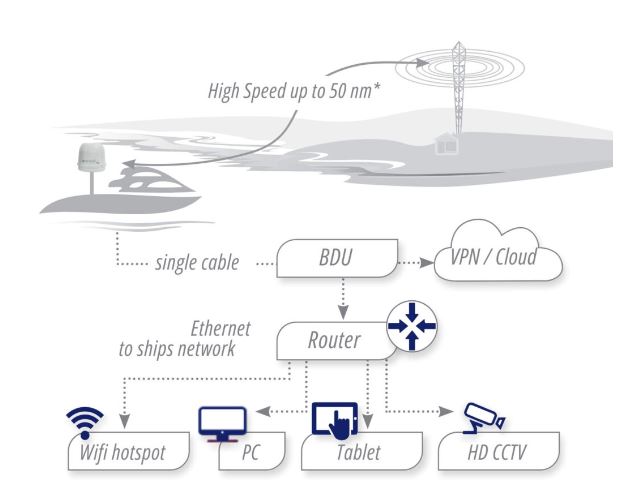
LTE broadband antennas have emerged as a game-changing technology in the realm of maritime communication. These sophisticated devices serve as the critical link between ships and land-based cellular networks, enabling vessels to access high-speed internet and maintain reliable communication channels even when far from shore.
At its core, an LTE broadband antenna is designed to capture and amplify cellular signals. Unlike traditional maritime communication systems that rely solely on satellite connections, LTE antennas can tap into terrestrial networks when within range, providing a more cost-effective and often faster alternative. This dual capability allows ships to seamlessly transition between satellite and cellular connections, ensuring continuous connectivity.
The technology behind LTE broadband antennas is complex, involving multiple elements working in harmony:
- MIMO Technology: Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) systems use multiple antennas to improve performance and reduce errors in signal transmission.
- Adaptive Beamforming: This technique allows the antenna to focus its signal in the direction of the nearest cell tower, maximizing reception and transmission quality.
- Frequency Aggregation: LTE antennas can combine multiple frequency bands to increase bandwidth and improve data speeds.
- Advanced Signal Processing: Sophisticated algorithms help filter out noise and interference, ensuring clearer communication.
These technological advancements have made LTE broadband antennas increasingly popular in the maritime industry, offering a level of connectivity previously unattainable at sea.
Key Features of Modern LTE Broadband Antennas for Maritime Use
Modern LTE broadband antennas designed for maritime use boast several key features that make them ideally suited for the challenging marine environment. These antennas are engineered to withstand the harsh conditions at sea while delivering optimal performance.
One of the most crucial aspects of maritime LTE antennas is their robust construction. Manufacturers prioritize creating compact, lightweight, and durable antennas that can withstand extreme weather conditions, including high winds, salt spray, and intense UV radiation. The materials used in these antennas are typically corrosion-resistant, ensuring longevity even in the most demanding maritime settings.
Another essential feature is the antenna’s omnidirectional capability. This allows the antenna to receive signals from multiple directions, which is critical for vessels that are constantly changing their orientation relative to cell towers. Some advanced models even incorporate smart switching technology, automatically selecting the best available network to ensure optimal connectivity at all times.
Key features of modern maritime LTE broadband antennas include:
- Weather-resistant design: IP66 or higher rated enclosures to protect against water ingress and dust
- Wide frequency range: Typically covering 4G/LTE bands from 600 MHz to 3.7 GHz
- High gain: Often ranging from 5 dBi to 12 dBi, depending on the model
- Low power consumption: Efficient designs that minimize drain on ship’s electrical systems
- Easy installation: Many models feature simple plug-and-play setups
- Integrated GPS: For location tracking and navigation assistance
- Compatibility: Designed to work with various routers and modems used in maritime settings
These features combine to create antennas that not only survive but thrive in the maritime environment, providing ships with reliable high-speed internet access that was once thought impossible at sea.
The Impact of High-Speed Internet on Maritime Operations
The introduction of high-speed internet, facilitated by LTE broadband antennas, has had a profound impact on maritime operations. This technological advancement has transformed various aspects of life and work at sea, enhancing efficiency, safety, and overall quality of life for crew members.
One of the most significant impacts has been on operational efficiency. With high-speed internet, ships can now transmit real-time data about their location, cargo status, and mechanical conditions to shore-based operations centers. This constant flow of information allows for better route planning, predictive maintenance, and more efficient logistics management. For instance, ports can better prepare for a ship’s arrival, reducing turnaround times and increasing overall efficiency in the shipping industry.
Safety at sea has also been greatly enhanced by improved connectivity. In emergency situations, high-speed internet enables quick communication with rescue services and allows for the transmission of detailed information, including video feeds, which can be crucial in coordinating rescue efforts. Additionally, telemedicine services have become more feasible, allowing crew members to consult with medical professionals onshore for health issues that don’t require immediate evacuation.
Furthermore, the availability of high-speed internet has opened up new possibilities for environmental monitoring and compliance. Ships can now transmit real-time data on emissions and fuel consumption, helping companies to optimize their operations for greater sustainability and ensure compliance with increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
The impact of high-speed internet on maritime operations can be summarized in the following table:
| Area of Impact | Benefits |
| Operational Efficiency | Real-time data transmission, improved route planning, predictive maintenance |
| Safety
|
Enhanced emergency communication, telemedicine services |
| Environmental Compliance
|
Real-time monitoring of emissions and fuel consumption |
| Business Operations
|
Improved communication with onshore teams, remote troubleshooting |
As LTE broadband antennas continue to evolve and improve, their impact on maritime operations is expected to grow, further revolutionizing the industry and bringing the connected world to the high seas.
Breaking Down the Numbers: Current and Future LTE Speeds at Sea
The advent of LTE broadband antennas has dramatically increased internet speeds available at sea, but understanding the current capabilities and future potential of this technology is crucial for maritime operators planning their communication strategies.
Currently, LTE broadband antennas can provide ships with impressive data transfer rates. Many systems offer download speeds of up to 150 Mbit/s and upload speeds reaching 50 Mbit/s. These speeds are sufficient for most modern maritime applications, including video conferencing, large file transfers, and streaming services. However, it’s important to note that actual speeds can vary depending on factors such as distance from shore, weather conditions, and network congestion.
To put these speeds into perspective, consider the following comparisons:
- A 150 Mbit/s download speed allows for downloading a 1 GB file in approximately 53 seconds.
- With 50 Mbit/s upload speed, a 500 MB video file can be uploaded in about 80 seconds.
- These speeds easily support multiple simultaneous HD video streams, enabling crew members to use entertainment services or participate in video conferences without issues.
Looking to the future, the potential for even faster LTE speeds at sea is promising. Industry experts predict that future LTE broadband antenna systems could achieve upload speeds of up to 500 Mbit/s and download speeds reaching an impressive 1200 Mbit/s. These advancements would represent a significant leap forward in maritime connectivity.
The implications of such speeds are far-reaching:
- Enhanced Real-time Monitoring: Faster upload speeds would allow for more detailed and frequent transmission of ship data, improving operational efficiency and safety.
- Improved Remote Operations: Higher bandwidth could enable more sophisticated remote control and automation systems.
- Advanced Entertainment Options: Crew members could enjoy 4K streaming and potentially even virtual reality experiences during their downtime.
- Seamless Cloud Integration: Ships could more easily integrate with cloud-based services, improving data management and accessibility.
To illustrate the potential impact of these future speeds, consider the following table comparing current and future capabilities:
| Capability | Current LTE Speeds | Future LTE Speeds |
| Download Speed | Up to 150 Mbit/s | Up to 1200 Mbit/s |
| Upload Speed | Up to 50 Mbit/s | Up to 500 Mbit/s |
| 1 GB File Download | ~53 seconds | ~6.6 seconds |
| 500 MB File Upload | ~80 seconds | ~8 seconds |
| Simultaneous HD Streams | 5-7 | 40+ |
While these future speeds are exciting, it’s important to note that their realization will depend on various factors, including the development of more advanced LTE broadband antennas, improvements in cellular network infrastructure, and the expansion of coverage areas at sea.
As technology continues to evolve, LTE broadband antennas will play an increasingly crucial role in maritime communications. Their ability to provide high-speed internet access at sea is transforming the maritime industry, bringing ships closer to the level of connectivity enjoyed on land and opening up new possibilities for efficiency, safety, and innovation in maritime operations.
Ready to revolutionize your maritime communications? Explore the latest LTE broadband antenna solutions and take the first step towards enhancing your vessel’s connectivity.